|
SAFETY V. Ryan © 2001 - 2008 |
|||
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR SAFETY TEMPLATE SHEET | |||
|
|
|||
|
When you design a project, it is essential that it is safe
for people to use. Safety is normally covered in the research or development
sections of the design process. However, you should always refer to safety when
writing notes about existing products or your own ideas. Do not underestimate
how important this area of design is and make sure that you often mention safety
when looking at existing ideas or producing your own. |
|||
|
THE LEARNING DEVICE |
|||
|
|
This is an example of a learning toy based on a jigsaw. When all the pieces are placed in the correct position the electronic circuit is completed and lights flash in sequence and a tune is played by a musical circuit. |
||
|
|
The pieces are placed one by one into a frame that is part of the base. In this photograph the track for the circuit can easily be seen. An important aspect of any project, especially one for a young child, is to ensure that it is entirely safe for any child to use. The factors listed below are some of the safety points that should be kept in mind when designing and making. |
||
| The example below has some safety aspects that need to be considered during the design process: | |||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
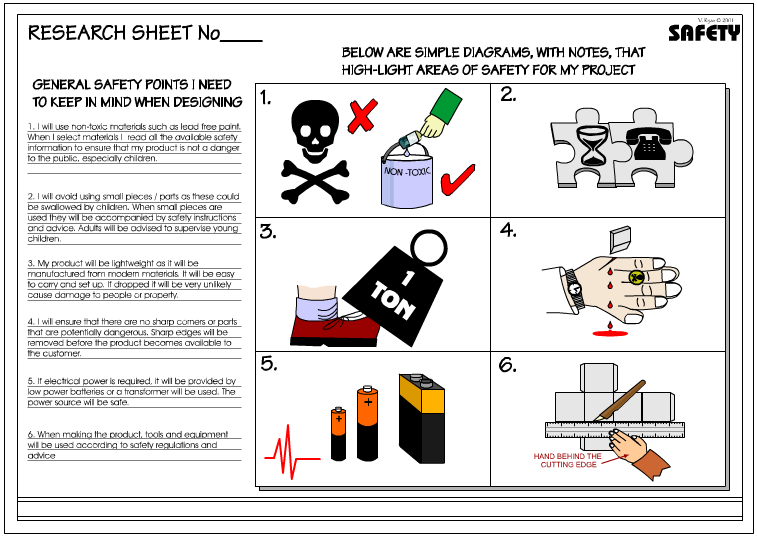
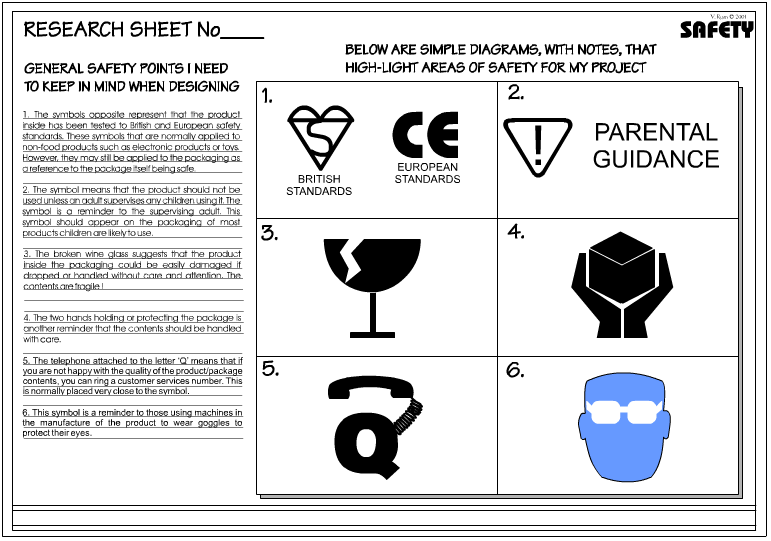
| You may need to consider other aspects of safety. Can you think of any that apply to your project? List them below. | |||
|
FURTHER INFORMATION |
|||
|
Safety is an essential aspect of research. The processes, equipment and materials used to make the final product must be safe for those involved in the manufacturing of the product. The final product must not put the customer in danger, in any way. Safety can only be assured if the project is planned and research carefully. Testing and evaluating prototypes and models is also important as these should raise safety issues and lead to modifications to the original design. |
|||
|
1. Look at existing products
and identify aspects that may be a danger. Suggests solutions /
improvements. |
|||
| TO 'ZOOM IN' CLICK RIGHT MOUSE BUTTON | |||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
SUGGESTIONS:
|
|||
|
LESSON STARTER/EXERCISE - SAFETY
|
|||
|
CLICK HERE FOR MORE EXAMPLE SAFETY SHEETS
|
|||
|
CLICK HERE FOR DESIGN PROCESS INDEX PAGE
|
|||