V.Ryan © 2019
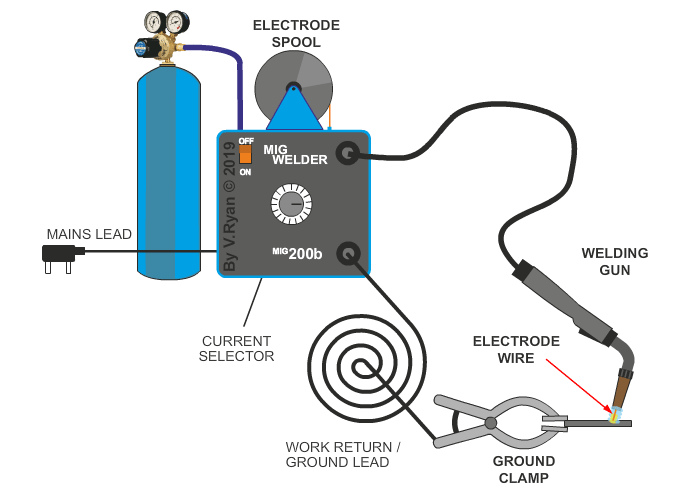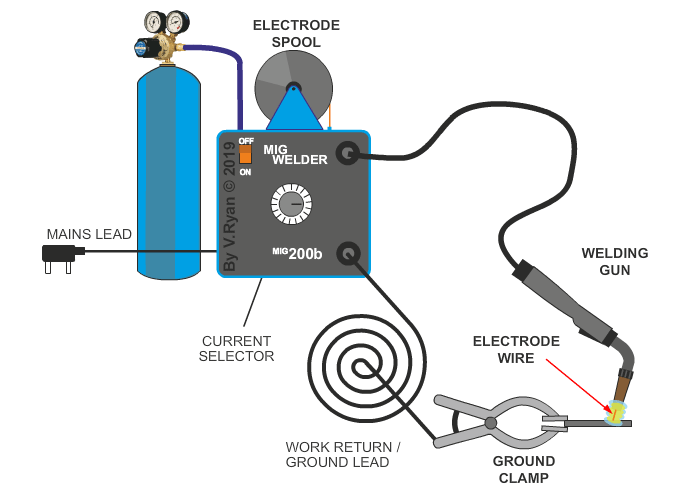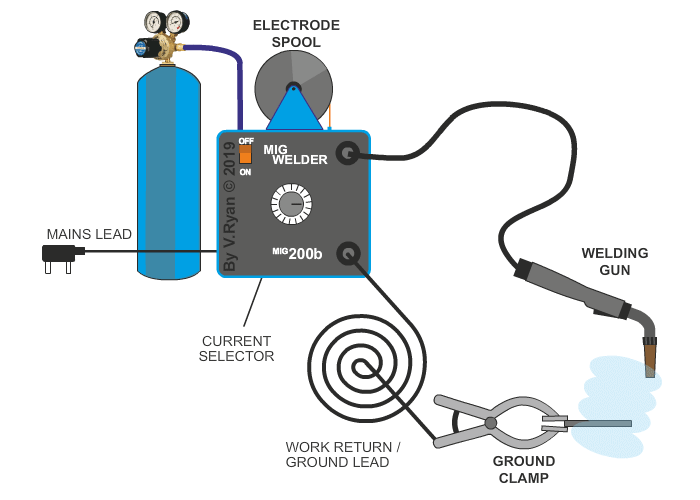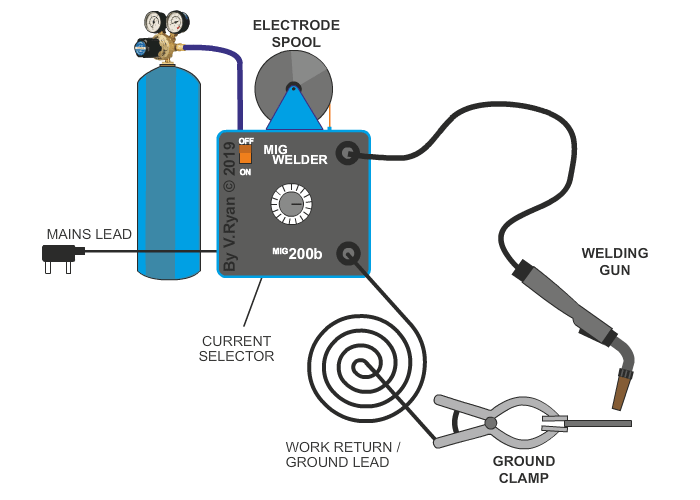
MIG welding has many industrial applications. The electrode is a continuous stream of wire, with a direct current source, fed at a continuous rate through the welding gun. Carbon dioxide gas is supplied directly to the welding zone, which acts to protect the area from atmospheric contaminants. The wire electrode, produces an ‘arc’, in the same way as electric arc (stick) welding, which heats the welding area and fuses the wire electrode with the base metal (metal being welded). MIG welding is ideal for aluminium, mild steel, stainless steel, copper and copper alloys.
MIG welding is much faster than electric arc welding (stick welding) and can be used to weld a wide range of metals and alloys. Longer welds can be achieved, as the electrode ‘wire’ is fed continuously from rolls, which makes this technique cost effective. The welds are cleaner than those produced by ‘stick’ welding, due to the nature of the protective gas.
However, MIG welding can only take place in a controlled area, without drafts and certainly not in the open air. This is because, it is important that the carbon dioxide gas is not disrupted.
Safety equipment: Suitable protective welding visor, to protect from Arc UV light, welding gauntlets, protective apron and gloves / gauntlets. Welding curtains should be set up around the welding area, to protect people working in the surrounding space, from the effects of Arc UV light.