| Below are some examples that show how relays can be used as part of a practical circuit. As stated in the first information sheet, the relay is normally used to switch ‘on’ another circuit. | |
|
RAIN ACTIVATED ALARM |
|
|
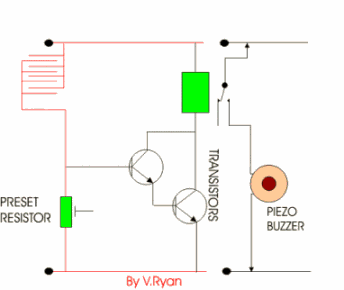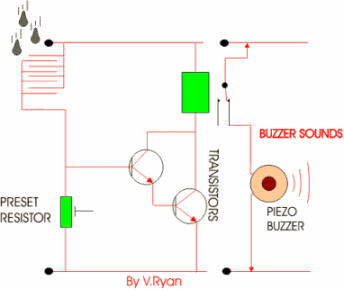
This circuit is simple in its operation, if it rains the
relay is ‘energised’ (switched). This could be part of a rain detection
system. The rain falls onto a small sensor which allows current to flow from
positive to negative. Current also flows into the base of the transistors
and the relay is energised. In turn, a second circuit is switched on and the
piezo buzzer sounds. This circuit could be used to warn of rain so that the
washing could be collected in before it gets too wet. |
|
|
|
|
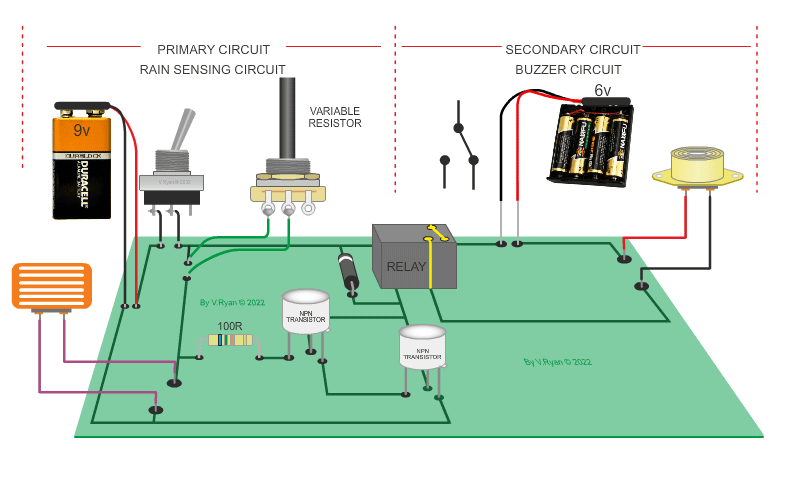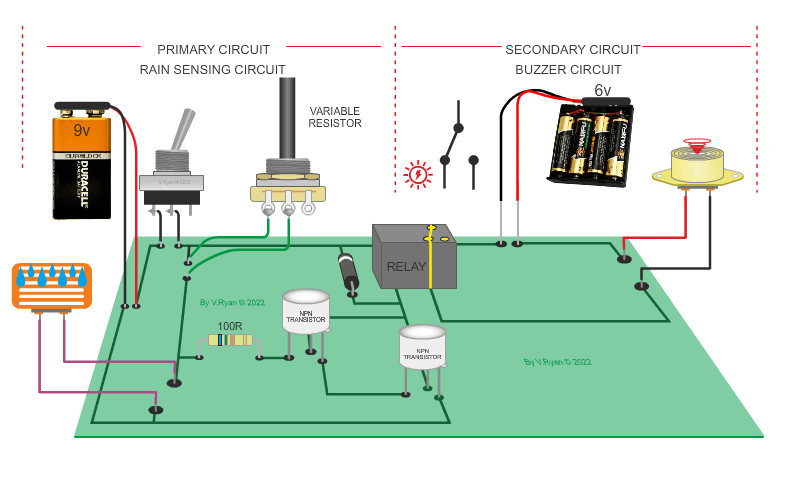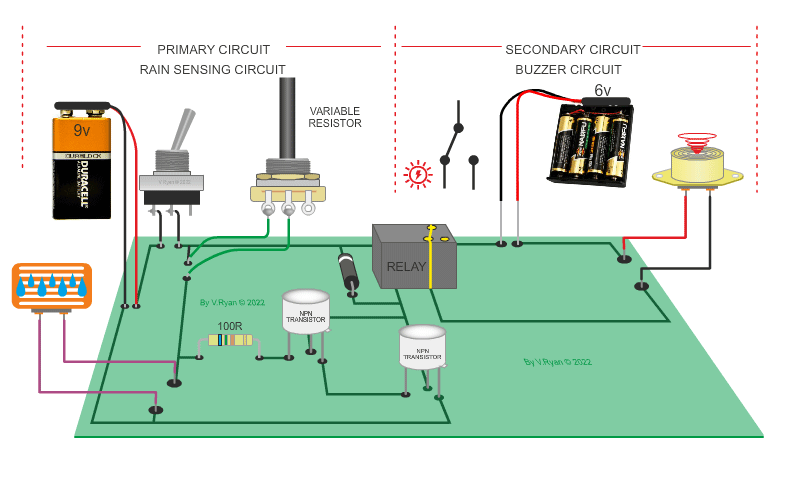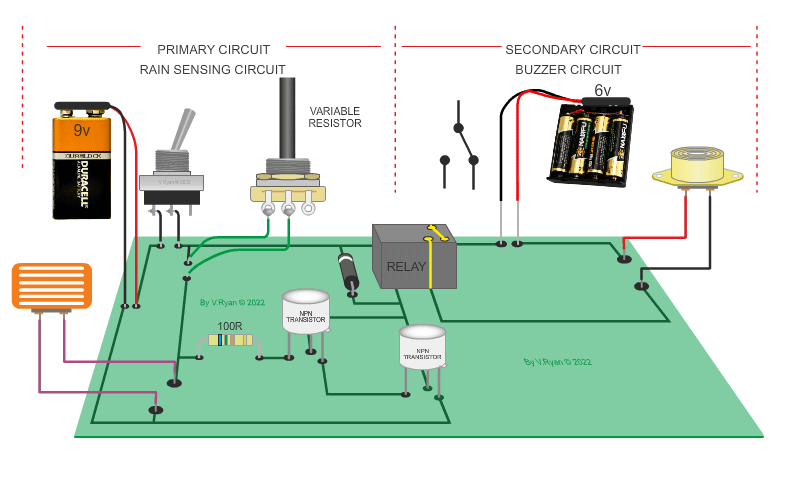
| PICTORIAL REPRESENTATION OD THE RAIN SENSING CIRCUIT | |
| (Notice that the transistors aare protected with a resistor and the relay is protected by a diode.) | |
 |
|
|
THE ZN 1034 PRECISION TIMER AND RELAY |
|
|
|
|
|
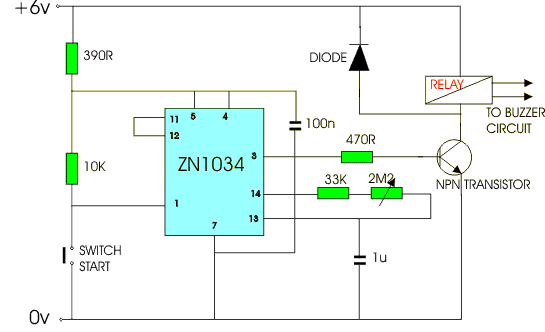
The ZN 1034 integrated circuit is a
precision timer. It is an extremely useful chip and often is used in
conjunction with a relay. In this circuit when the switch is pressed the
relay is ‘energised’ for a period of between two and one hundred minutes,
depending on how the variable resister has been set. This means the buzzer
sounds for that amount of time. |
|
|
|
|