| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE | |
| HEALTH AND SAFETY FOR THE CONSUMER | |
| V. Ryan © 2003-2021 | |
|
The designer and manufacturer of a product have a
moral obligation to make sure that a customer / consumer is not injured
by it when used. Also, both the designer and manufacture must be
socially and environmentally responsible. Putting it in simple terms,
the final product must not be a danger, cause damage to people in any
way or damage the environment.
|
|
|
QUESTIONS: 1. Ed the
Handyman has designed a ridiculously
dangerous toy for a child. It is a mechanical dogs head. When the
handle/stick is banged on the floor the fierce jaws, with sharp teeth,
snap shut at supersonic speed. What is dangerous about this toy? |
|
|
|
|
|
2. Ed heís a
Handyman has designed a hair brush. He
claims it will help hair grow especially if the user has very little
hair. However, when used it pulls hair out by the roots instead of
combing it properly. |
|
|
|
|
|
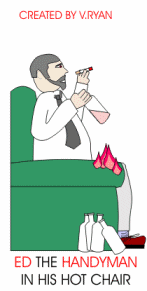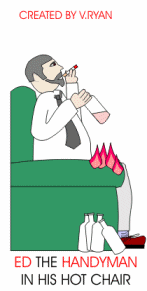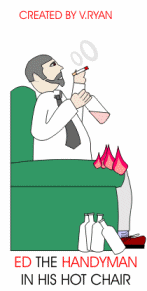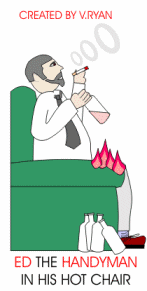
3. Ed the
Handyman has little commonsense, he drinks
and smokes. The hot ash from his cigarette falls onto his old armchair
and sets it alight easily. Ed has failed to check if the chair is made
from fire retardant fabric and foam. He found the chair on a rubbish tip
and decided to use it himself. |
|
|
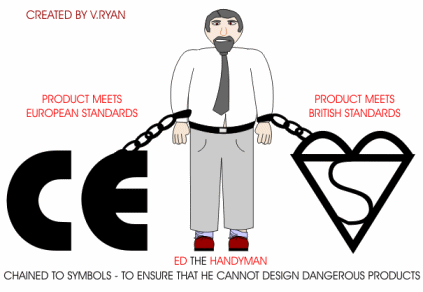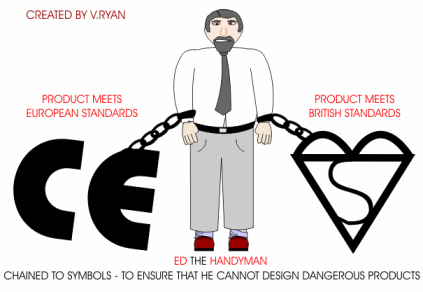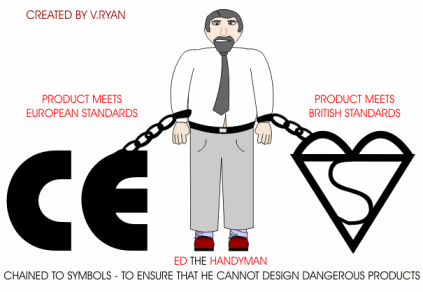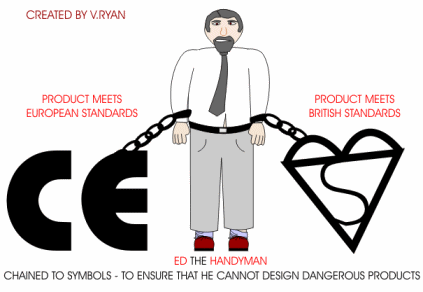
Ed the Handyman designs products that are so dangerous that he has been chained to two important safety symbols, by the police. These symbols can only be applied to products that have been tested thoroughly by agencies such as the British Standards Institute (BSI). The BSI test a wide range of products, checking that they work safely and perform exactly as the manufacturer states. If they pass all the tests, then the manufacturer is allowed to put the symbol on their product. This means that a customer can easily check that the product has passed safety tests. |
|
|
|
|
|
4. Go to a toy shop and list toys that have these two symbols on them. Do you consider each of the toys to be safe? |
|
|
|
|