| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET | |
| PDF FILE - LITHOGRAPHY | |
|
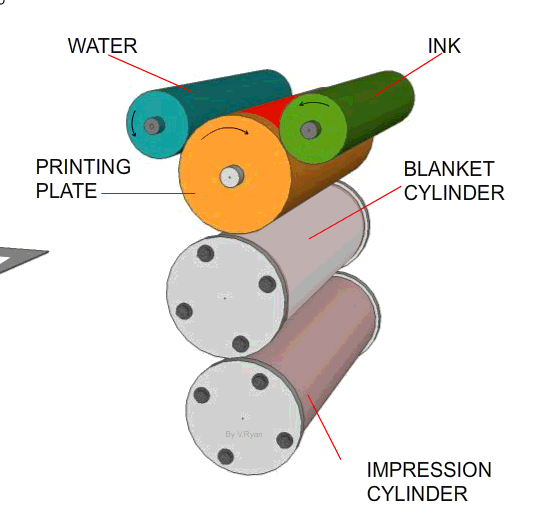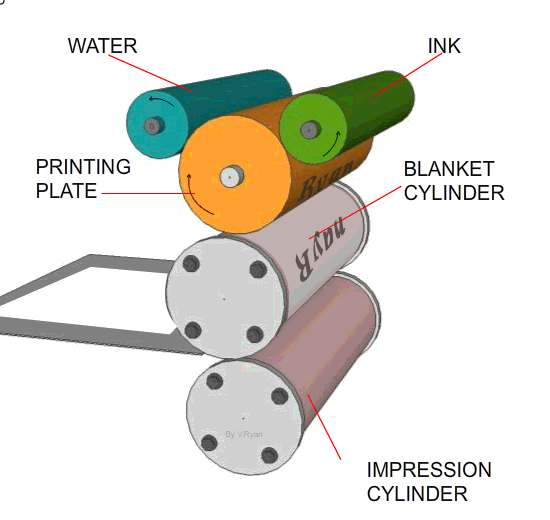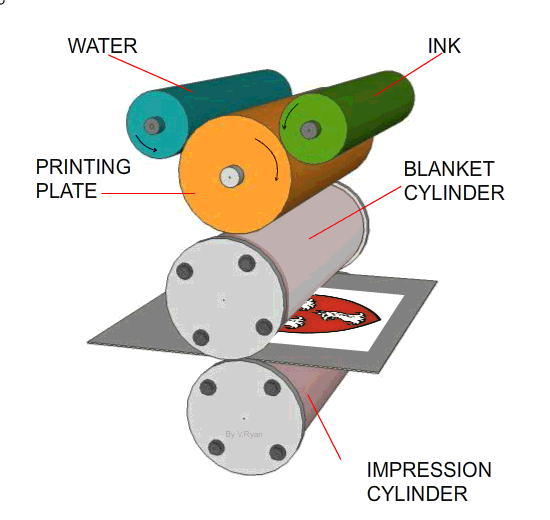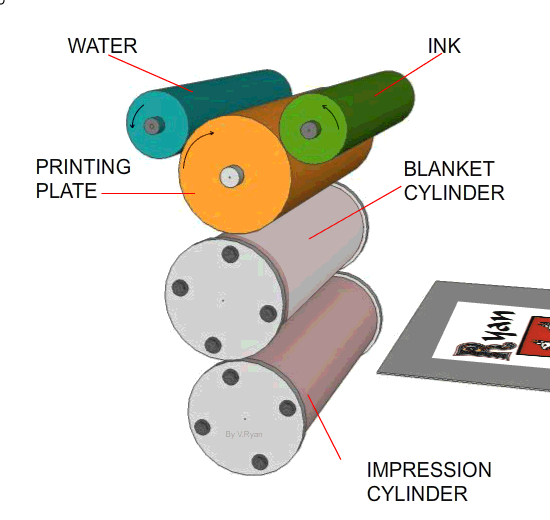
Lithography is mainly used by commercial printers, printing companies that will print thousands of copies of the same item, in one production run. Lithography machines can print on both sides of paper/card and they rely on four basic colours; yellow, cyan (type of blue), magenta (type of red) and black. This is also known as the CYMK process. |
|
 |
|
| Example of Lithography as used in the packaging industry | |
 |
|
|
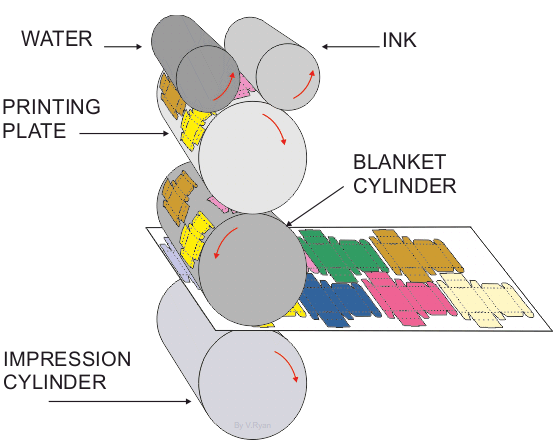
1. The printing plate has the image to be printed, in relief, on its surface (the image stands out slightly from the printing plate surface). 2. The printing plate is kept dampened. Ink is applied to the plate but it is repelled from the dampened surfaces which are the non-image areas. 3. As the printing cylinder rotates the ink is transferred to the rubber blanket cylinder. 4. The ink, now on the rubber blanket cylinder, is pressed onto the paper or card as it is pulled through the machine. (The paper is trapped between the blanket cylinder and the impression cylinder - these pull the paper through the machine)
|
|
|
With some modern lithography printing machines the image is put onto the printing plate by shining ultra violet light through a negative (similar to a photograph negative). The plate is coated with a chemical which allows the ink (made from oil) to attach to the image area. If different colours are needed for the final print - the same card/paper will be sent through the machine and each time different negatives and colours will be applied. This is done until the print, which may be a poster, is completed. |
|
|
Draw a simple diagram of a lithography printing machine and add notes to help explain the stages involved. |
|
|
|
|