|
|
|
|
HOW TO WRITE A SPECIFICATION V. Ryan © 2001-2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE SPECIFICATION SHEETS | |
| PDF FILE - PLAIN SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE | |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR SPECIFICATION EXERCISE | |
|
The ‘specification’ is probably the easiest part of the design process although it is one that pupils tend to neglect or write incorrectly. It is usually a list of points, with each point referring to the research work. In the specification you need to show what you have learnt from the research that you collected and presented in the research section. |
|
|
1. The materials I will use will be
compressed polystyrene, pine and MDF because my research clearly shows
that this combination will improve my solution. 2. The overall shape will depend on the ergonomics of the hand. I will base the dimensions on statistics worked out as part of my research. 3. I intend to use a colour scheme based on red and blue because the questionnaire I carried out shows these are the most popular colours. 4. The solution will have the following functions: (List exactly what the solution will do). 5. The solution will stand on a desk / fixed on a wall. 6. I will need the following tools/machines to manufacture my solution: a lathe, drilling machine, hand files, a vacuum former etc...... 7. The solution is aimed at the 12-15 age group as my research suggests this would be the most successful market. |
|
|
Write a specification for a project of your choice. You should be able to list quite a number of points in your specification but always say how your research has helped you. Usually this section is a list of approximately 10 points. |
|
|
|
|
|
FURTHER INFORMATION |
|
|
The specification is probably the easiest section of a design project, if all the research has been carried out. The specification draws on the information collected and presented during the research section. The specification is a number of straightforward statements, made clearly outlining the nature of the project to be designed and manufactured. If the research section has not been completed fully, the specification will also be lacking. |
|
|
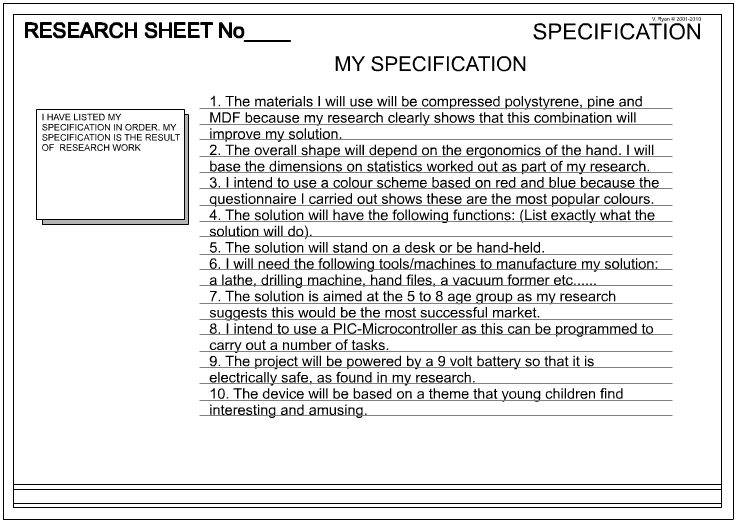
The example specification shown opposite has been
written for a project regarding designing a small electronic/mechanical
toy for young children. |
|
| SAMPLE LAYOUT | |
 |
|
| SAMPLE SPECIFICATION | |
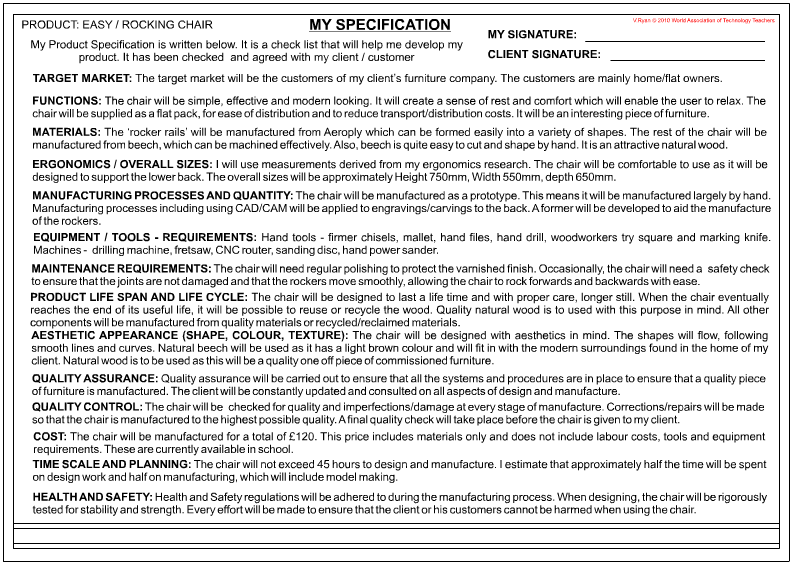
| This specification has been written for a rocking chair. | |
 |
|
| ALTERNATIVE - LAYOUT | |
 |
|
| SUGGESTIONS: A. Write a rough specification first and ask other pupils / teachers to read it. B. Look carefully at each statement and keep the English as clear and simple as possible. C. Limit the statements to between 7 to 12 points (maximum). D. Ensure most points refer directly to your research. E. Do not fall behind in your work as you will find it difficult to catch up later. |
|
| CLICK HERE FOR DESIGN PROCESS INDEX PAGE | |
|
|
|
