| |
| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE |
| |
| 555 TIMER EXAMINATION QUESTIONS - 2 |
| |
| V. Ryan © 2006 - 2009 |
| |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE VERSION OF
EXERCISE SEEN BELOW |
| |
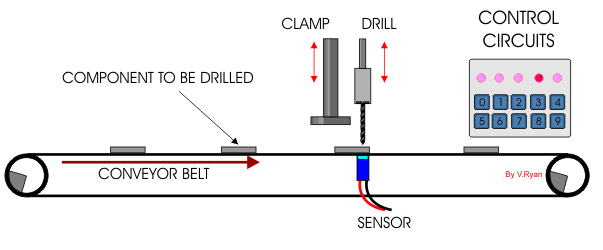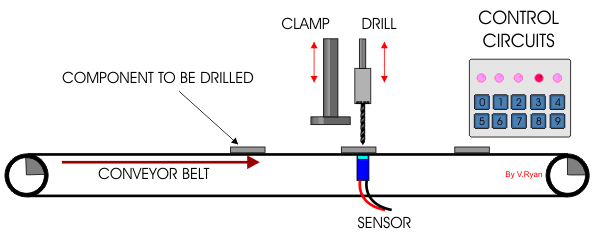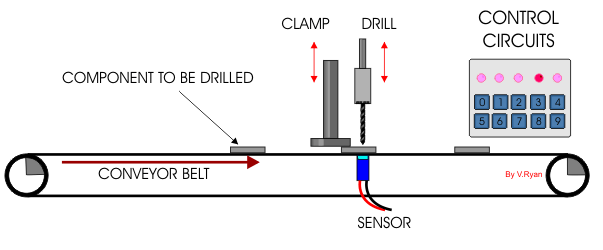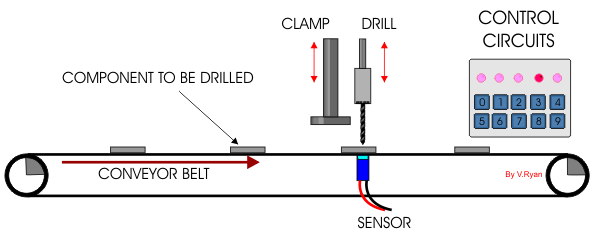
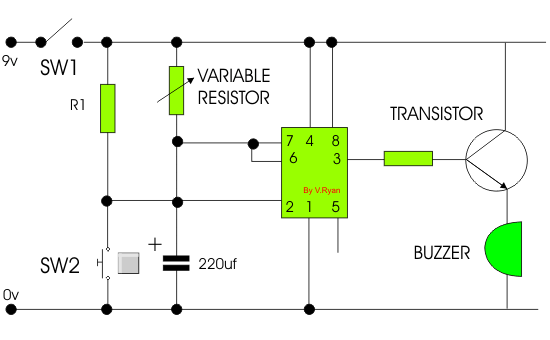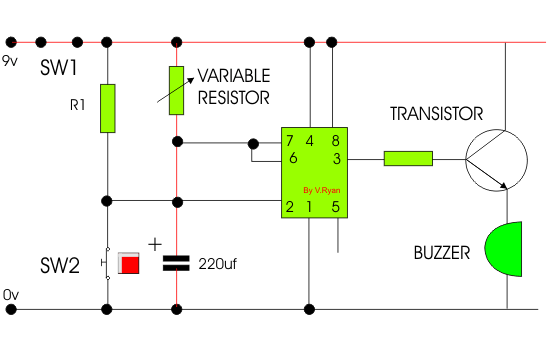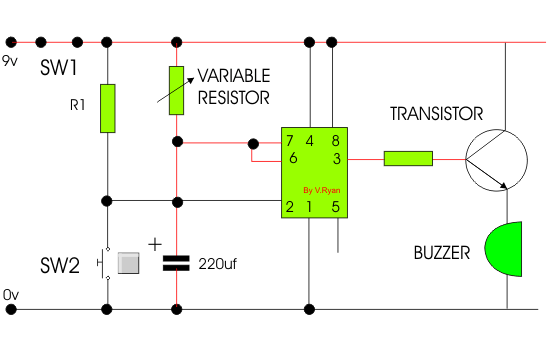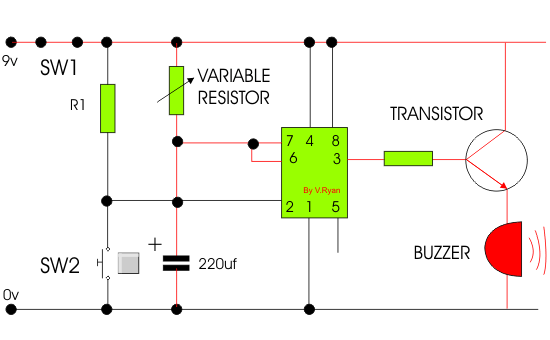
| 1. The following
question is based on the 555 monostable circuit. The circuit shown is
part of a production line and controls the timing sequence. The
automated production line is shown below. Parts / components move along
the production line where they are sensed, clamped down, drilled and
then released, moving down the production line again. The 555 monostable
circuit controls the timing of the entire production line. |
| |
 |
| |
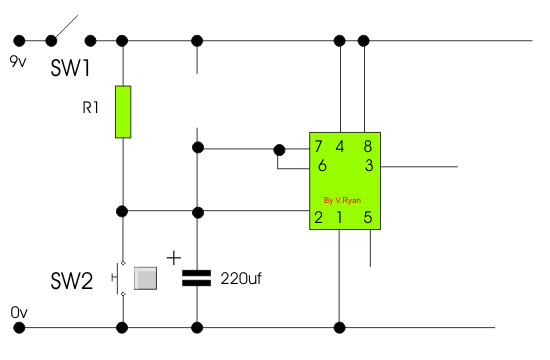
The timer circuit is found inside the control circuit
box. The incomplete circuit diagram is found below. Add the following
components to complete the timer circuit:
A. 0v and 9v supply
B. A variable resistor for altering
the length timing sequence.
C. A buzzer that sounds during the
timing sequence. |
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER |
| |
 |
| |
| 1. Explain how your completed
circuit works. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER |
| |
| When SW2 is pressed current flows into pin 2 of the 555 timer starting
the timing sequence. Current flows from pin 3 into the transistor,
allowing current to flow from positive to negative, sounding the buzzer.
The buzzer sounds for the entire timing sequence. |
| |
| 2. What is the
role of the variable resistor and capacitor? |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER |
| |
| Both components are key to the length of time of the
timing sequence. If a resistor and capacitor of higher values are used
then the timing sequence is longer. |
| |
| 3. The 555 timer is an IC. What does
IC mean? |
| |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER AND FURTHER
INFORMATION |
| |
| IC means ‘Integrated Circuit’ - click here for further
information |
| |
|
|
| |
| 4. The 555 timer has a DIL layout. What
does DIL mean? |
| |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER AND FURTHER INFORMATION |
| |
| DIL means ‘Dual In-line. This means that there are two parallel lines of
pins - click here for further information |
| |
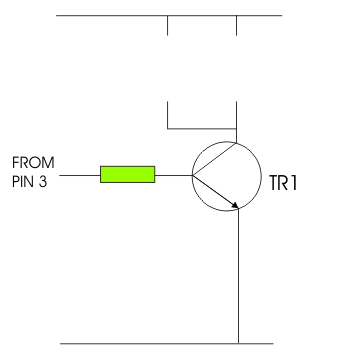
5. It has been
found that the sound emitted by the buzzer is too low. A circuit
designer has suggested that a relay be added. The circuit also needs
protecting by the addition of another component placed in parallel with
the relay. (See layout below)
Complete the circuit diagram by adding the relay and a suitable
additional ‘protecting’ component. |
| |
 |
| |
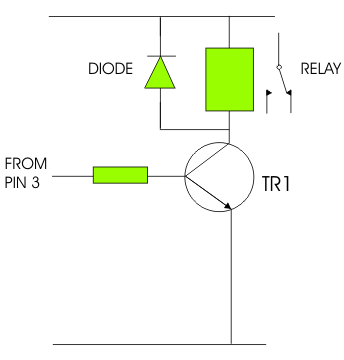
| POSSIBLE ANSWER |
| |
 |
| |
| 6. Name the component that protects
the circuit and explain how it does this. |
| |
| NAME:_____________________________ |
| |
| How the component protects the circuit. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER |
| |
| NAME : DIODE |
| |
| How the component protects the circuit: |
| The diode is placed in parallel with the relay,
placed the opposite way round to its normal direction. When the relay is
switched off it can cause back E.M.F. This is current that is sent round
the circuit in the wrong direction. This ‘spike’ can damage sensitive
components such as transistors. The diode stops current flowing round
the circuit in the wrong direction. It acts like a one way valve. |
| |
| Click here for more on Diodes |
| |
|
|
| |
| 7. What is back EMF ? |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER |
| |
| E.M.F is Electro Motive Force. Back E.M.F is current
that is sent round a circuit in the wrong direction. This can damage
sensitive components such as transistors and integrated circuits. |
| |
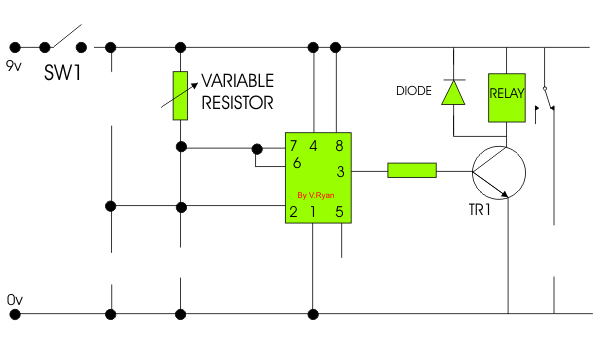
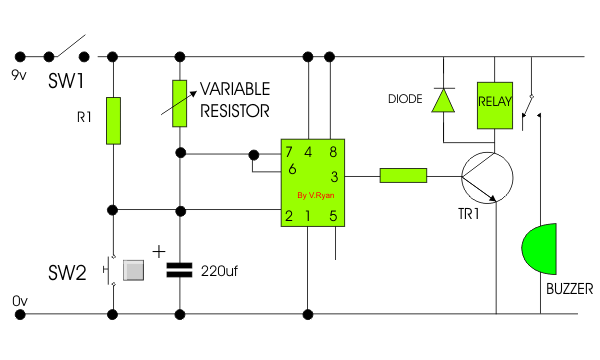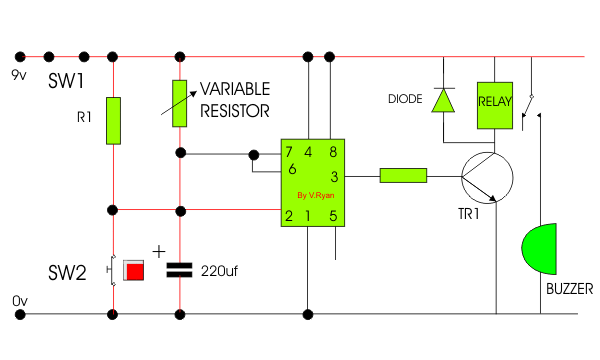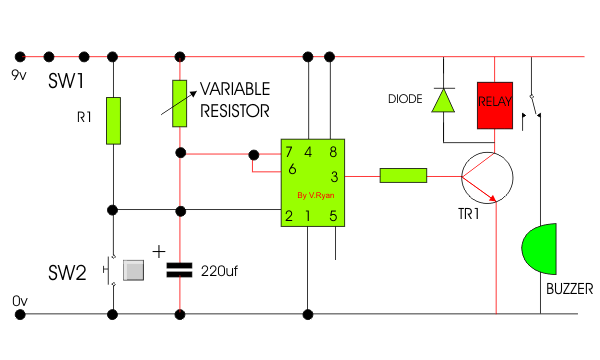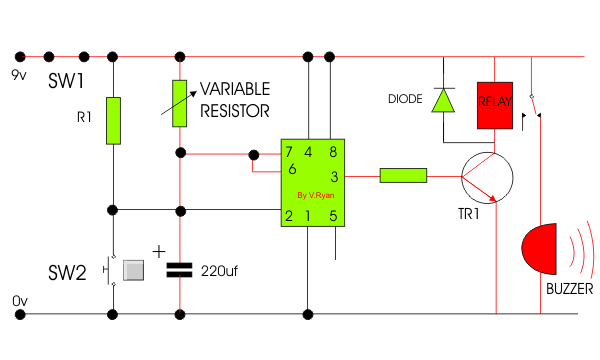
| 8. The incomplete
timer circuit is shown below. Some components are missing. Draw the
missing components in the correct positions, adding suitable labels. The
missing components are shown below the circuit diagram. |
| |
 |
 |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER |
| |
 |
| |
| 9. In the space
below explain how the entire circuit works. Include an explanation of
the key components and their role in the circuit. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| POSSIBLE ANSWER |
| |
When switch 1 is closed current is available for the
circuit. When switch 2 is pressed current flows into pin 2 of the 555
timer, starting the timing sequence. Current flows from pin 3 of the
timer into the base of the transistor allowing the relay to become
energised. The relay switches on the remaining part of the circuit by
allowing current to flow through the buzzer which sounds.
The diode protects sensitive components by preventing back E.M.F. The
combination of the variable resistor and the capacitor determines the
length of time the 555 timer counts. When the timer has finished
counting, current no longer flows from pin 3 and the buzzer stops
sounding. |
| |
| CLICK HERE FOR ELECTRONICS INDEX PAGE |
| |
| |







