Analogue signals
Digital signals
Examples of analogue systems include;
Old radios, megaphones and the volume control on old telephone hand sets.
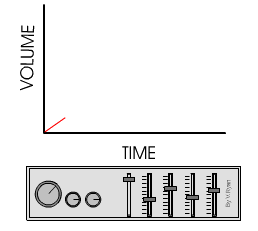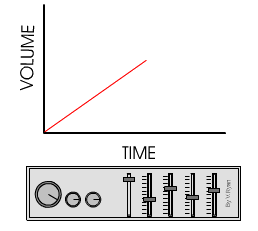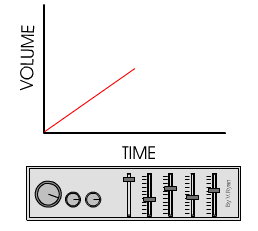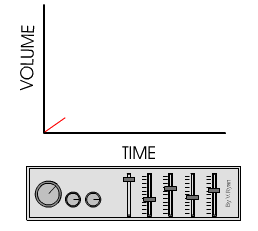
This graph is typical of analogue signals.
Digital Signals: Modern electronic products such as computers and mobile phones depend on digital signals. However, a good example of a digital signal is Morse Code. The signal is sent as a series of ‘on’ and ‘off’ pulses. The signal is either present or it is not. Morse code was introduced in 1837 by Samuel Morse, as a method of communication.
For further information on digital computers - see Bits and BYTES.
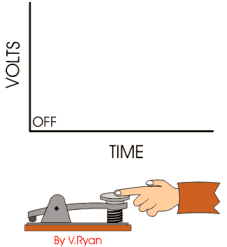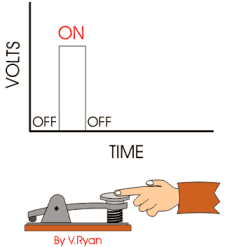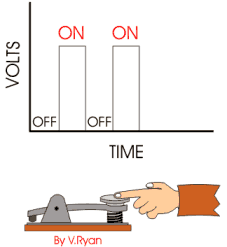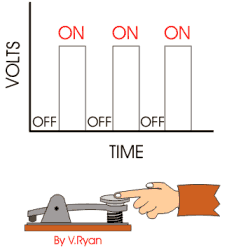
Both analogue and digital systems can be used as sensors. A thermistor is analogue as resistance slowly changes, a micro-switch is digital, as it is ‘on’ or ‘off’.
Computers are digital devices and the various electronic parts communicate using 1’s and 0’s.
1 = ON
0 = OFF