| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE | ||
| REVISION CARDS - SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS | ||
| V. Ryan © 2013 | ||
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET | ||
|
1. PARALLEL CIRCUITS 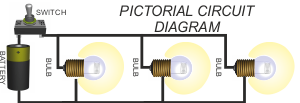 The circuit above/below shows three bulbs placed in parallel. This is a parallel circuit. Current can flow through each of the bulbs, without first having to flow through any others. If any of the bulbs fail, the others will still work as current can still flow through the rest of the circuit. 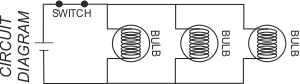 |
2. SERIES CIRCUITS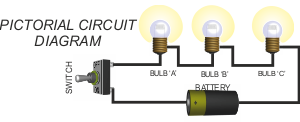 The circuit above shows three bulbs placed in series. This is a called a series circuit. Current flows through each of the bulbs in sequence. The more bulbs that are added, the less bright they shine. This is due to the resistance in each bulb. If any of the bulbs fail, current cannot flow through the circuit and the other components will not work. 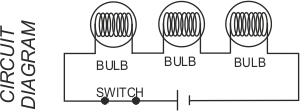 |
|
|
3. SERIES / PARALLEL CIRCUITS The circuit seen below has components arranged in parallel and series. 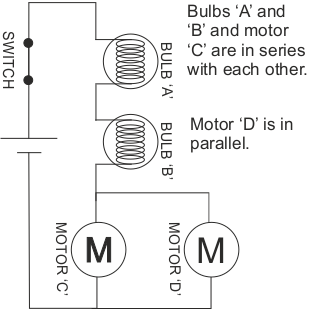 |
Most complex circuits are a combination of components arranged in series
and parallel (see Genie Microcontroller Circuit below) .Simple circuits
are often either parallel or series. |
|
| 1. Describe / explain two advantages of using bulbs / LEDs in parallel. 4 marks | ||
| 2. In a series circuit, composed of 2 bulbs / LEDs and a battery, what could happen if another bulb / LED is added? 2 marks | ||
| 3. If motor ‘D’ fails, in the circuit seen drawn on revision card 3, will the entire circuit fail? Underline the correct answer. 1 marks | ||
| YES / NO | ||
| CLICK HERE FOR ELECTRONICS INDEX PAGE | ||