| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE |
| COMPOSITE MATERIALS - CONCRETE |
| V. Ryan © 2010 |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET |
|
Concrete is a versatile and cheap material, with a vast range of applications around the home. Brick laying, constructing paths and driveways, foundations to buildings and walls, are some of the practical applications. Concrete has a similarly wide and varied range in industrial applications. Theses include; bridge construction, motorways, curbs, walkways and foundations to entire factories and industrial sites. |
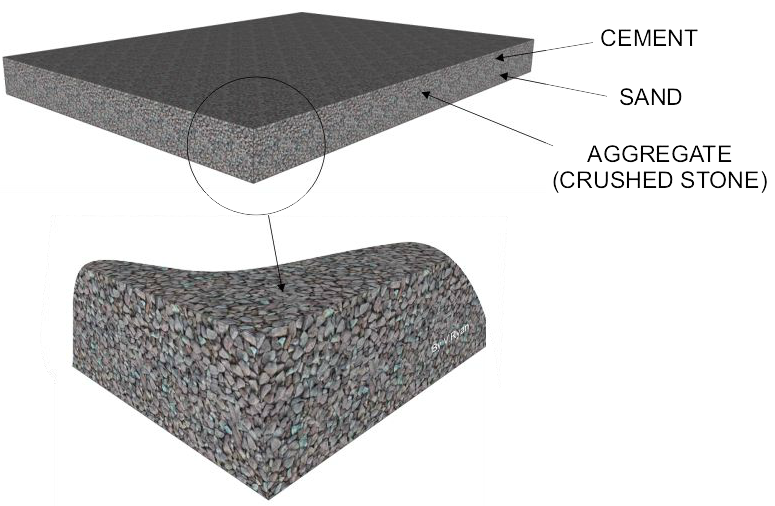
| Concrete is regarded as a composite material because it is composed of a number of materials that combine to form this versatile building material. Most concrete is made up of Portland Cement, aggregates (gravel, crushed stones) and sand. Water is added to the mix. |
|
Concrete can be purchased as precast products, such as paving stones.
These can be purchased from DIY stores or building suppliers. They are
usually laid on a firm foundation. Concrete can be purchased ready mixed and poured into an area prepared for a foundation. Alternatively, the component parts that make up a concrete mixture, can be mixed to produce ‘liquid’ concrete, on site. This can be poured to produce an area such as a driveway or foundations to a building. |
| The magnified view shows the component materials that make up the composite material known as concrete. The aggregate (crushed stone) is clearly seen. |
 |
| TYPICAL USES OF CONCRETE |
| GARDEN PONDS - PATHS - PAVING - WALLS - PILLARS/SUPPORTS - DRIVEWAYS - PATIOS - CONCRETE - CASTINGS - FOUNDATIONS - LAMP POSTS - BEAMS - ARTIFICIAL STONE |
| CLICK HERE FOR RESISTANT MATERIALS INDEX PAGE |
|