| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE |
| CONDUCTIVITY, DUCTILITY AND MALLEABILITY |
| V. Ryan © 2012 |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET |
| VIDEO - MATERIALS TESTING |
|
CONDUCTIVITY |
|
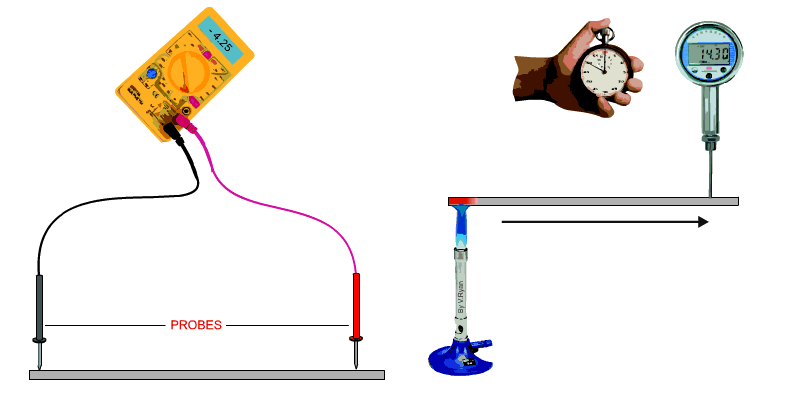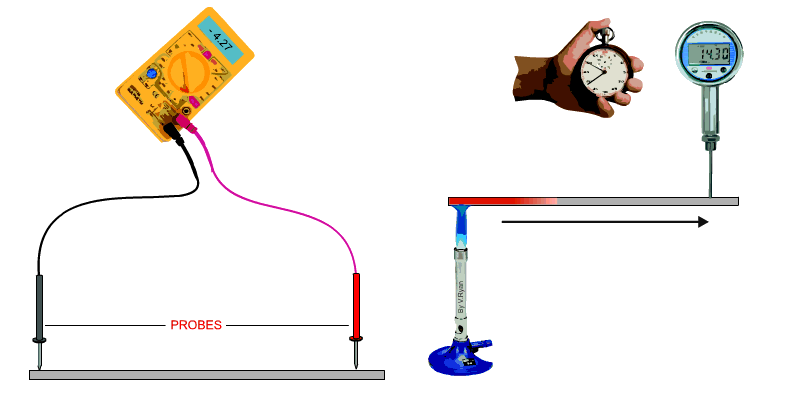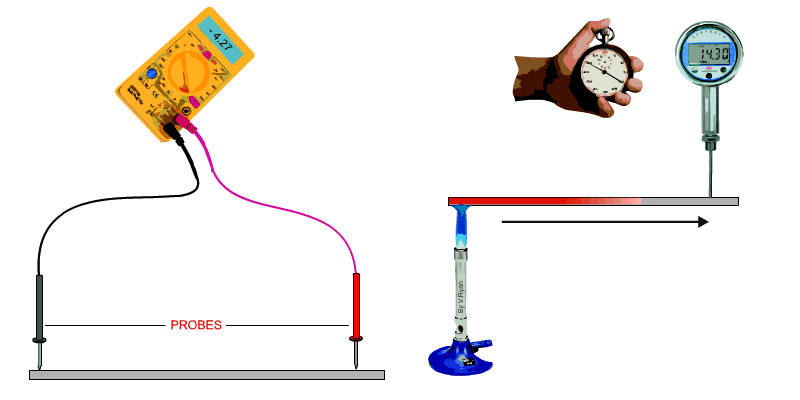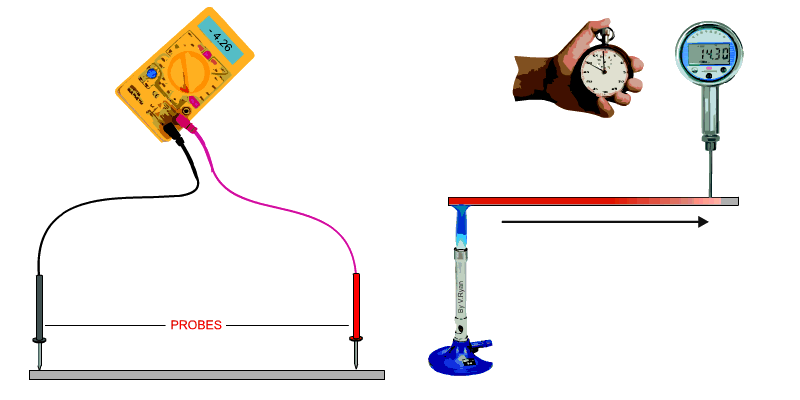
The conductivity of a material can be defined as, ‘the ability of a
material to conduct electricity or heat’. A test for electrical conductivity is seen below. A voltmeter is used to measure resistance. The probes are set to the same distance on each sample. The resistance is a measure of the materials conductivity. A test for heat conductivity/transfer is seen below. A bunsen burner is placed at one end of a piece of material and a temperature meter at the other end. The time it takes for the temperature to change at the opposite end of the material is recorded. If a selection of materials of the same length and section are tested in this way, their conductivity can be compared. |
 |
| DUCTILITY AND MALLEABILITY |
| The ductility of a material can be defined
as, ‘the ability of a material to change shape (deform) usually by
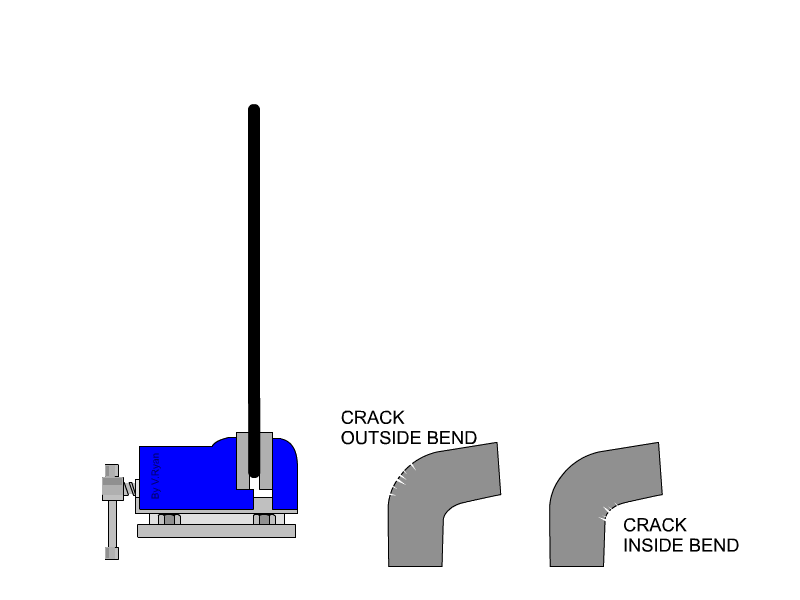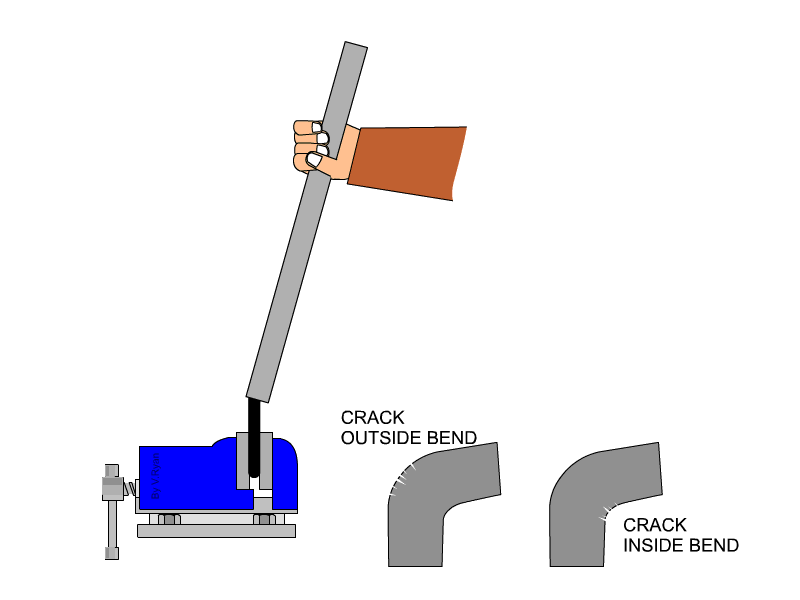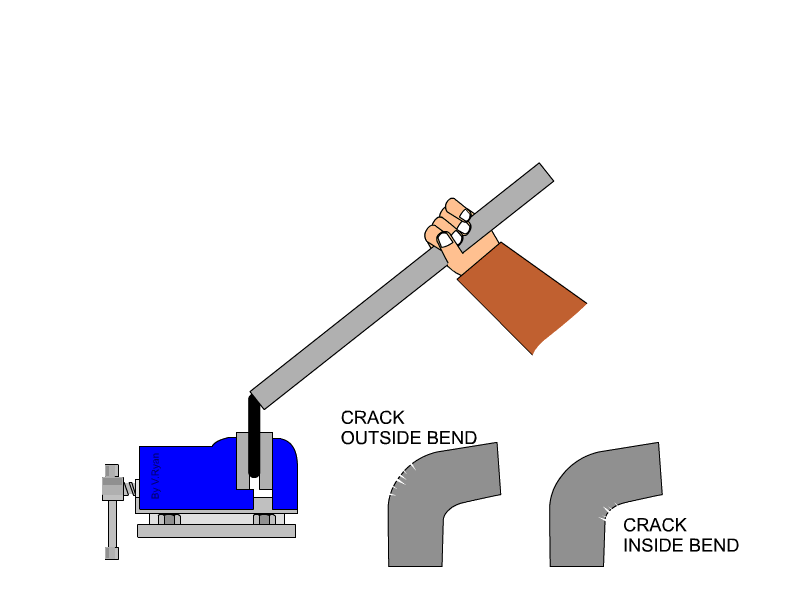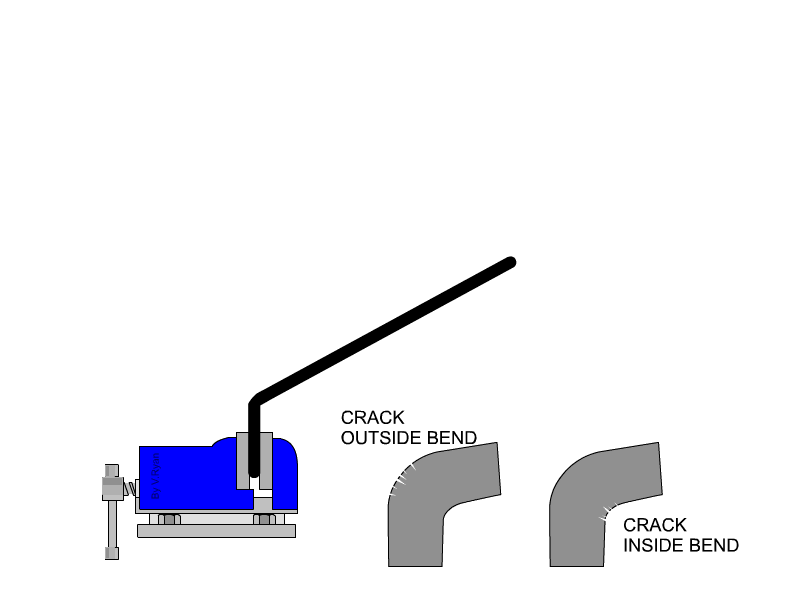
stretching along its length’. The malleability of a material can be defined as, ‘the ability of a material to be reshaped in all directions without cracking’. A piece of tube is placed over a piece of material and used as a lever. The material is folded to 90 degrees. Cracks / damage on the outside of the bend represents a lack of ductility. Cracks / damage on the inside of the bend represents a lack of malleability. |
 |
| CLICK HERE FOR RESISTANT MATERIALS INDEX PAGE |