| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE |
| PLYWOOD |
| V. Ryan © 2010 |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET |
|
Plywood is a composite material, although we often
consider it as a traditional working material. It is composed of
individual plies / veneers of wood. It is very strong due to the way the
plies are put together. The grain of each ply is positioned at ninety
degrees to the pieces of ply above and below it. The plies are glued
together with synthetic resin, making a very strong composite material.
Furthermore, plywood is usually constructed so that an odd number of plies
are used. Plywood is less likely to warp or split, due to this
construction. |
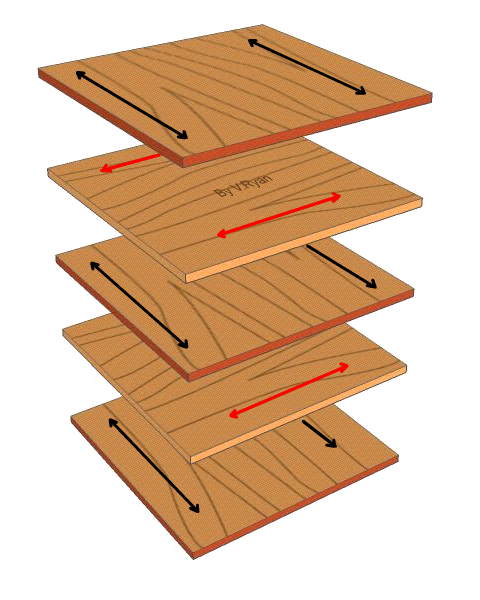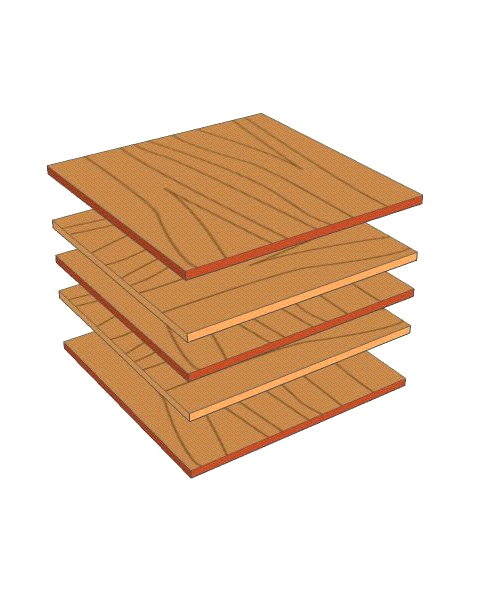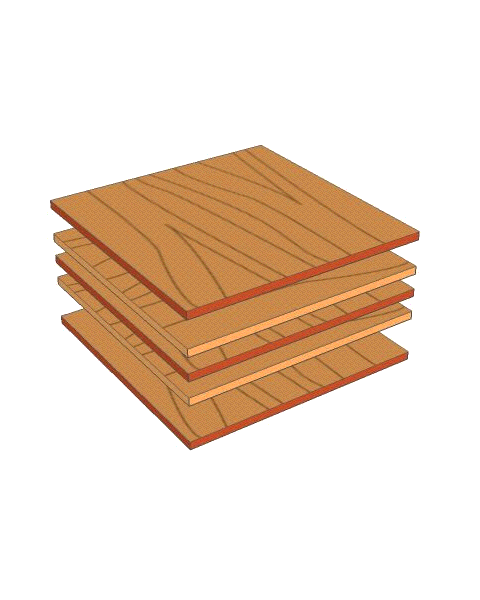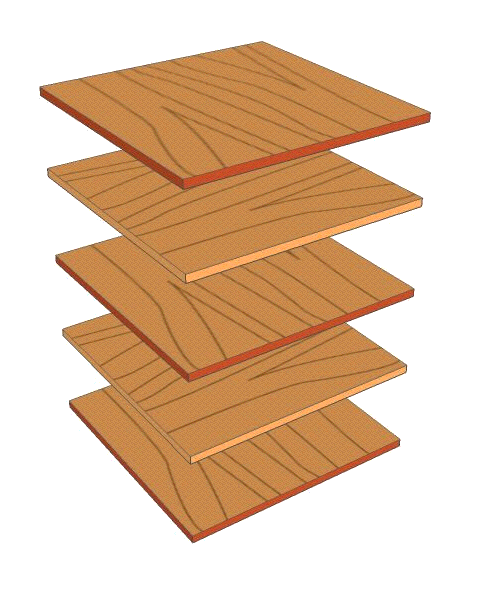
| The diagram below, shows the individual layers of plywood, called plies or veneers. Study the diagram, especially the grain. Each ply has its grain running at ninety degrees to the next layer, as indicated by the arrows.. |
 |
| The diagram below represents a board of plywood, composed of individual plies glued together with synthetic resin. Note the odd number of plies used. |
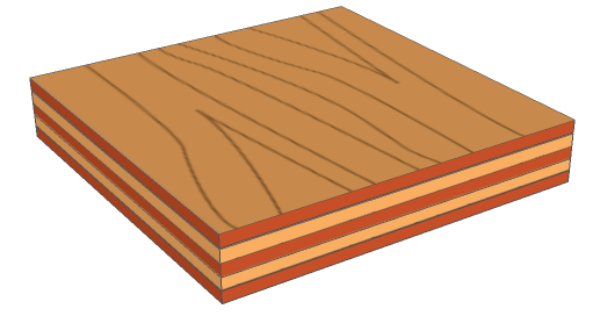 |
| CLICK HERE FOR RESISTANT MATERIALS IDEX PAGE |