| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE | |
| CAMS and FOLLOWERS | |
| V. Ryan © 2002 - 2024 | |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET | |
| CLICK HERE FOR POWERPOINT VERSION OF WORKSHEET | |
| Have you ever looked closely at a simple mechanical
toy ? If you have the opportunity to study one closely you will see that
it is made up of mechanisms, usually including CAMS. Can you name any mechanical devices that use cams as part of its movement? |
|
|
|
A CAM changes the input motion, which is usually rotary motion (a rotating motion), to a reciprocating motion of the follower. They are found in many machines and toys |
|
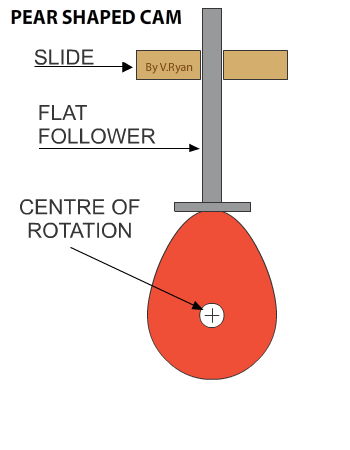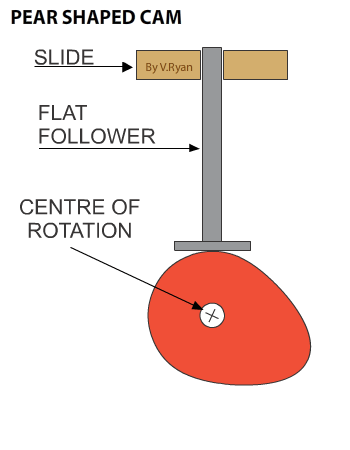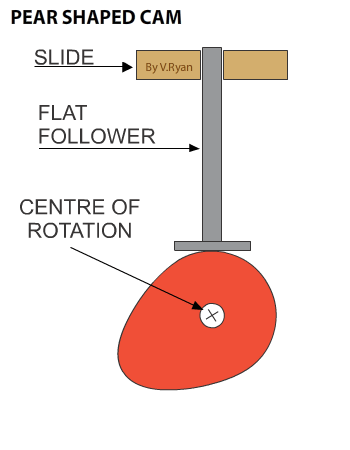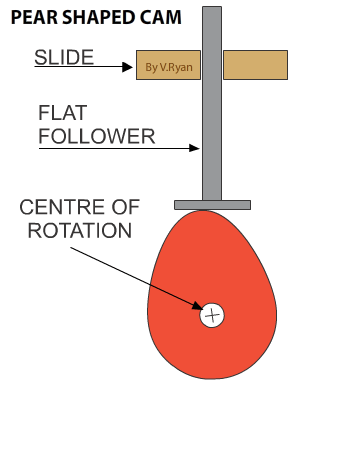
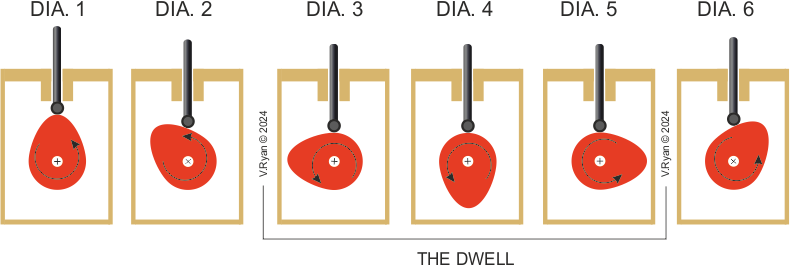
A CAM has two parts, the FOLLOWER and the CAM PROFILE. Diagrams one to six show a rotating cam pushing a follower up and then allowing it to slowly fall back down. |
|
 |
|
|
Diagram 1 shows the cam is in a vertical position. It slowly rotates in an anticlockwise direction. As it rotates the follower drops down (diagram 2). Diagrams 3 to 5 show no change in the height of the follower, called the ‘dwell’ (a characteristic of pear shaped cam profiles). The dwell is when the cam continues to rotate, but its shape means that there is no change in the position / height of the follower. Diagram 6 shows the follower rising again. |
|
|
KEY PHRASES |
|
| ONE CYCLE | One rotation/revolution of the cam. |
| DWELL |
When the cam rotates but the follower does not rise or fall. |
| THE RISE |
That part of the cam that causes the follower to rise. |
| What do you think is the 'FALL' ? | |
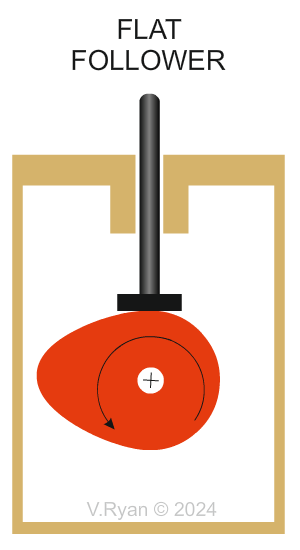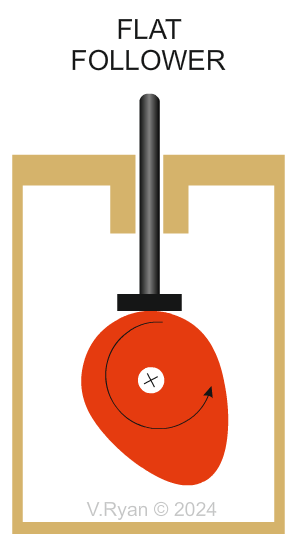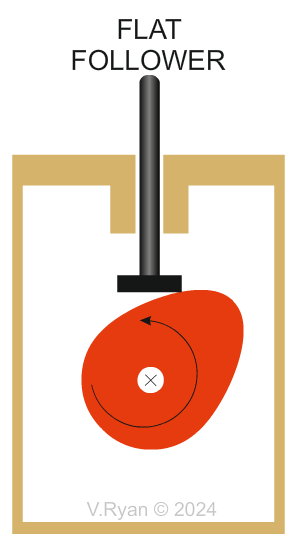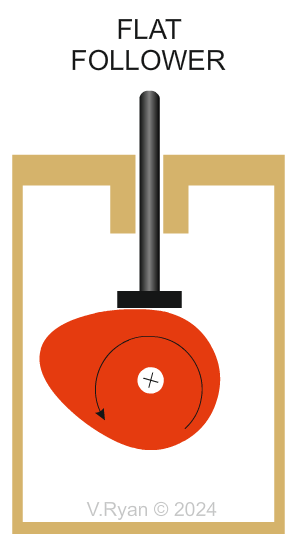
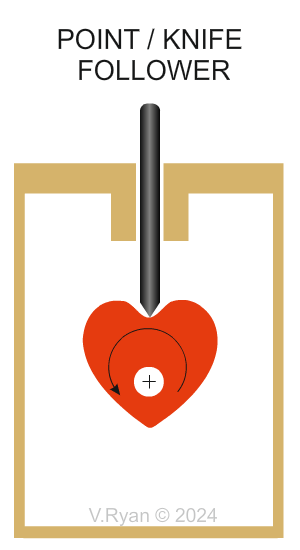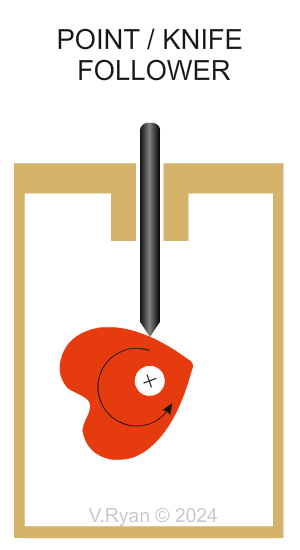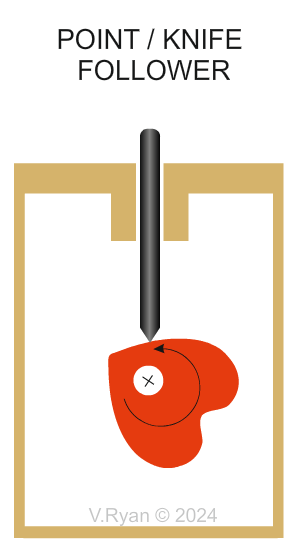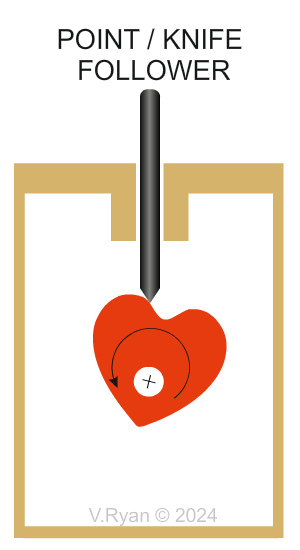
| TYPES OF FOLLOWER | |
| There are different types of follower but they all slide or roll on the edge of the cam. Various types are shown below. | |
 |
|
Why are Flat followers are selected? The size of the flat follower’s surface means that jamming is unlikely, because weight is spread over a wider area. The flat’s contact area, is in the centre which means weight is efficiently distributed. Flat followers are relatively simple and uncomplicated. They are easy and cheap to manufacture. |
|
 |
|
Why are Point or Knife followers are selected? Only the tip of the follower touches the rotating cam, minimising friction. This makes this type of follower ideal where accuracy of movement is required. (Accurate Movement and Minimised Friction). Most knife followers have replacement tips because ‘wear and tear’ is an issue. This sometimes means that the mechanism is out of action, until the tip is replaced. Regular, planned maintenance is required with this type of follower. |
|
 |
|
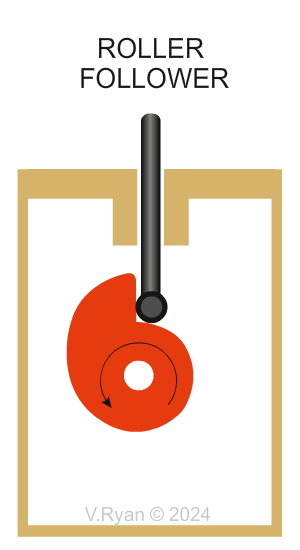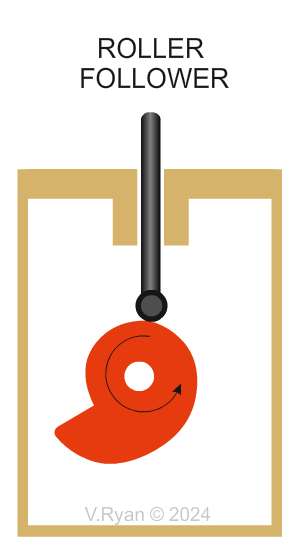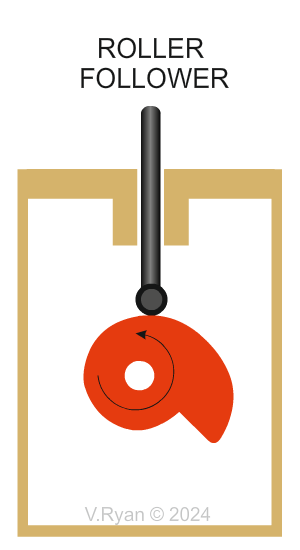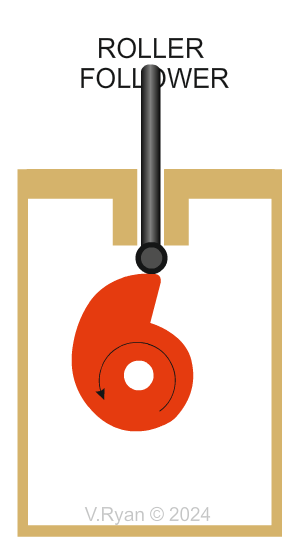
Why are Roller followers are selected? The roller rotates smoothly when in contact with a turning cam profile. This reduces friction leading to operating efficiently. This type of roller is ideal when heavy loads are involved, unlike a knife follower. The roller follower copes very well with rapid changes in the shape of the cam profile, as shown above with the ‘drop’ cam. |
|
 |
|
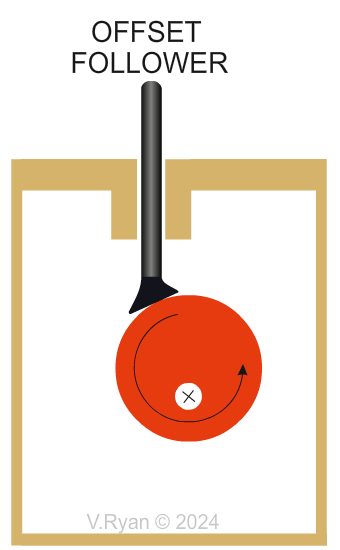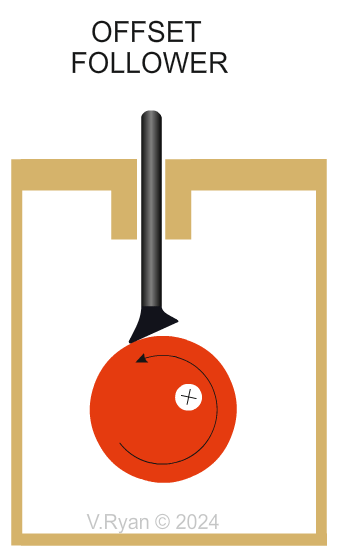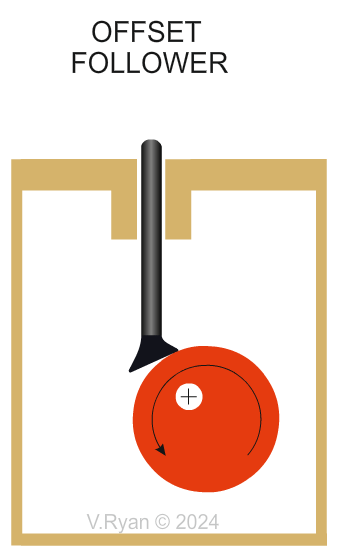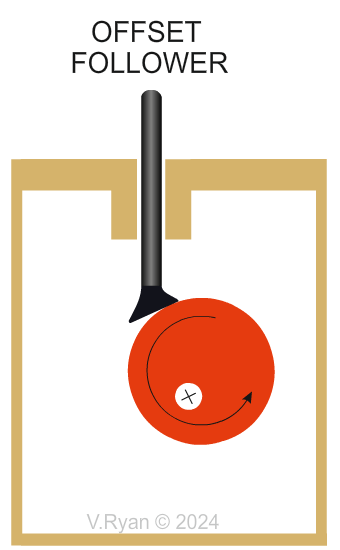
Why are offset followers are selected? This type of cam handles side forces really well, as shown above with the offset circular cam. The weight applied to the follower is distributed across the flat when making contact with the cam. Offset followers are used in mechanisms, that output precise control. |
|
|
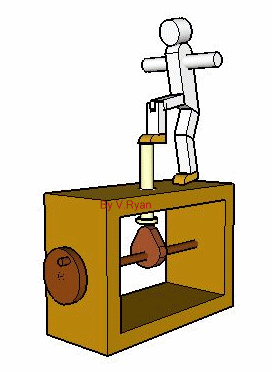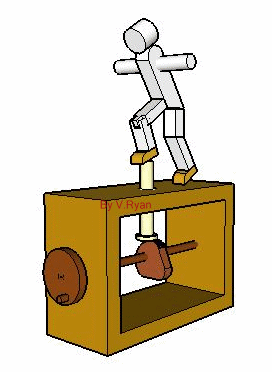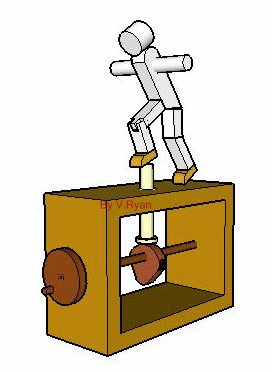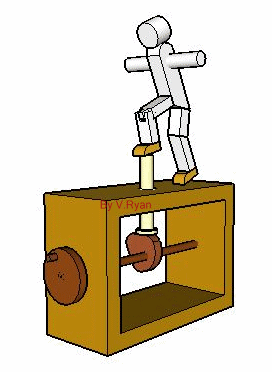
The cam seen below is a 'pear shaped cam'. As the handle is turned the cam profile rotates. The model moves forwards and backwards as a result. The movement is gentle although the faster the handle is turned the faster the movement of the model becomes. |
|
 |
|
|
|
|