DIRECT METAL LASER SINTERING (DMLS)
V.Ryan © 2019-2023
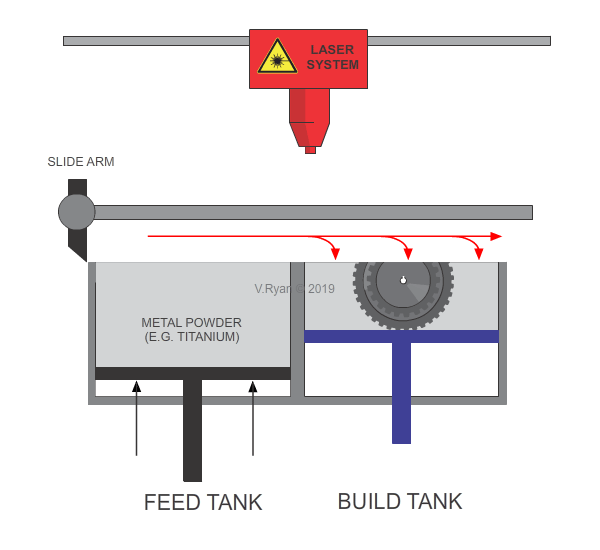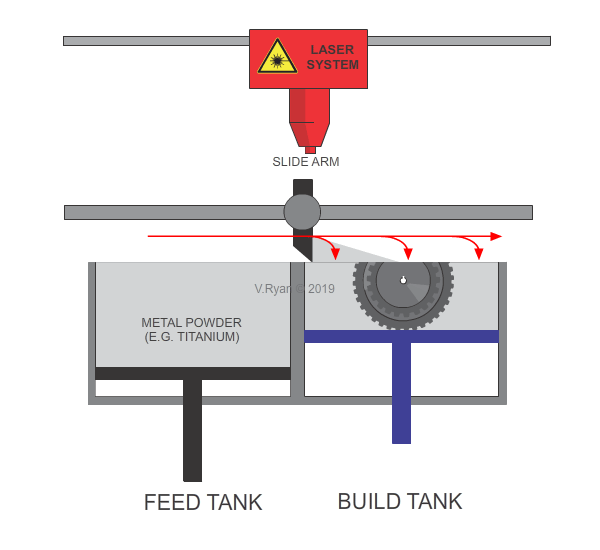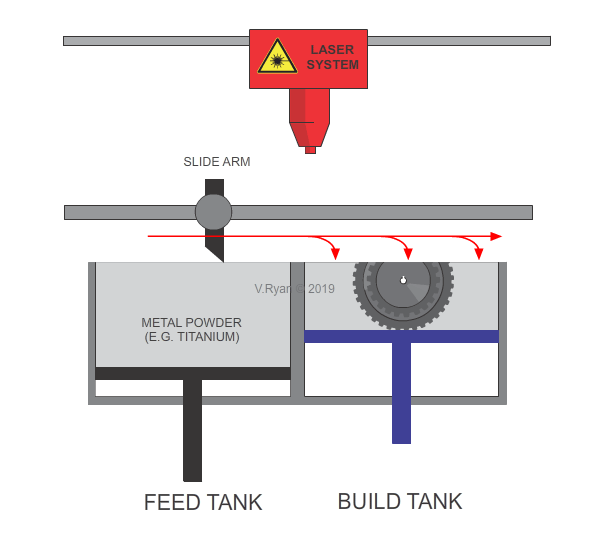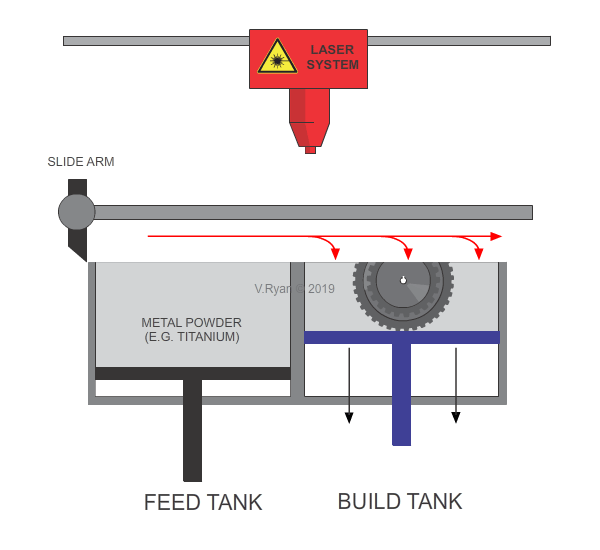
The feed tank moves upwards by a distance equal to a layer of powder.
The slide arm pushes the layer of metal powder from the feed tank and deposits it equally across the build tank.
A laser fuses the powder, forming one layer of the product.
The build tank drops down the distance of another layer.
This process is repeated continually, until the 3D product is complete.
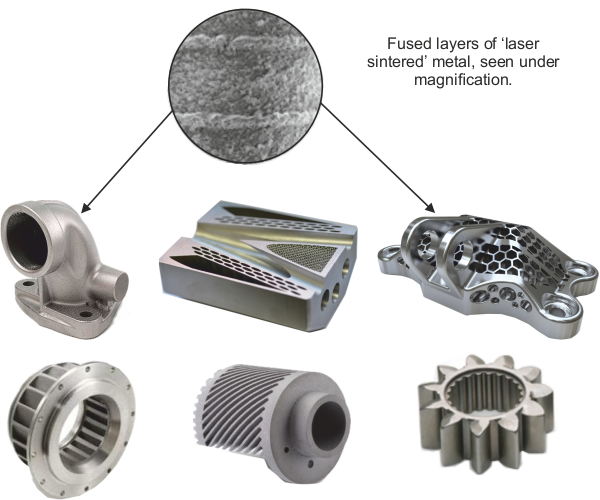


No need to manufacture a complex and expensive mould.
Capable of manufacturing extremely complex designs / components, not capable of being manufactured in any other way.
A self contained manufacturing process.
Ideal for final prototyping and one-off or short batch manufacture.
Does not require continual supervision by a skilled technician / engineer.
The design does not require the addition of supporting parts, as the powder supports the layers as they are produced.
A wide range of metal powders are available and can be used with this industrial process.
Not suitable for large production runs.
Not cost effective for ‘simple’ engineered products.
The density of the final metal component, is likely to be lower than one manufactured through conventional engineering processes.
Laser manufacture requires high levels of energy consumption.
The finished component may have a level of porosity, allowing liquids and gases to be absorbed.